Infographic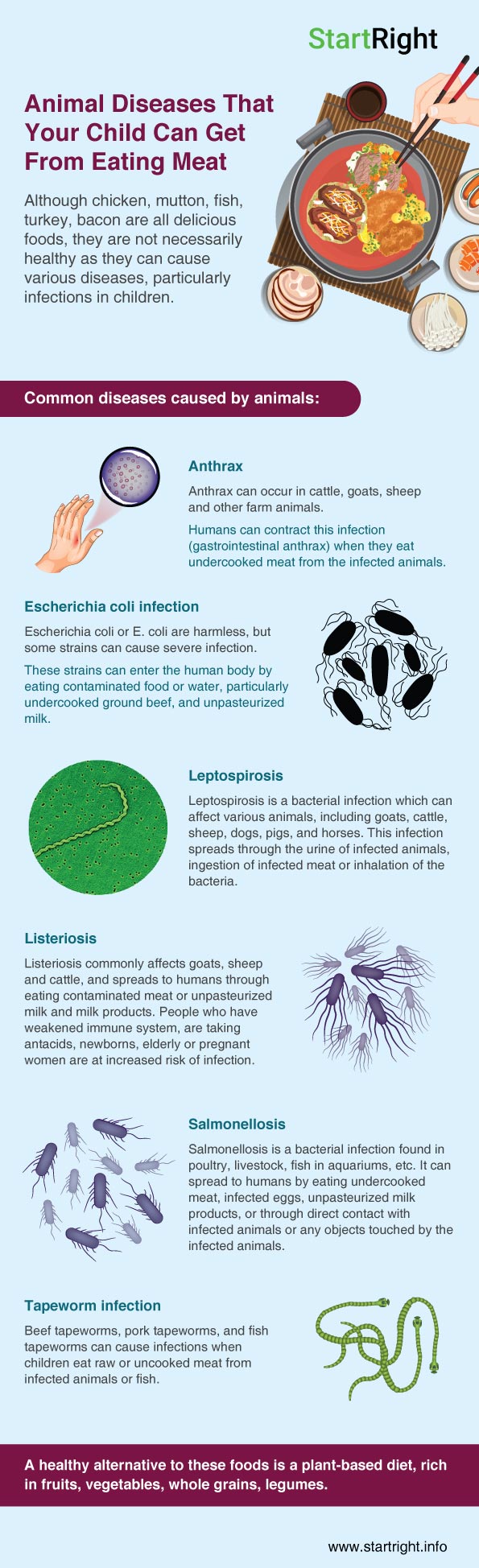 Click Here | Chicken, mutton, fish, turkey, bacon are all delicious foods, which may have been hard for you to give up and adopt a plant-based diet. However, you may be aware that some of these foods do provide nutrients for growing children; for instance, chicken is a good source of protein, some fishes have good amount of omega 3 fatty acids, etc. Although, these foods may be nutritious, they are not necessarily healthy as they can cause various diseases, particularly infections in children. Some of these diseases are discussed in this article. |
Anthrax
Anthrax is a disease caused by a bacteria which forms spores (highly resistant, dormant structures against adverse environmental conditions). This disease can occur in cattle, goats, sheep and other farm animals. Humans can contract this infection (gastrointestinal anthrax) when they eat undercooked meat from the infected animals. This can present as fever, chills, sore throat, painful swallowing, swelling of the neck or neck glands, stomach pain, diarrhea, etc. The bacteria can also enter the body through a wound in the skin, or by inhaling the spores from infected animal products like hair, wool, leather, etc.
Escherichia coli infection
Escherichia coli or E. coli are bacteria that normally live in the intestine of human beings and animals. Most strains of E.coli are harmless, but some strains can cause severe infection. These strains can enter the human body by eating contaminated food or water, particularly undercooked ground beef, and unpasteurized milk. People can also be infected when they come in direct contact with infected animals, objects that are contaminated by the infected animal or from infected people. These infections can cause serious disease in people. The symptoms of infection include severe stomach cramps, bloody diarrhea, vomiting, and low fever. Young children and the elderly are more prone to a severe complication of this infection called hemolytic uremic syndrome, a type of kidney failure.
Leptospirosis
Leptospirosis is a bacterial infection which can affect various animals, including goats, cattle, sheep, dogs, pigs, and horses. This infection is most commonly spread through the urine of infected animals, but people can also be infected by coming on in direct contact with infected animal tissues, ingestion or inhalation of the bacteria. Some people with the infection may not have any symptoms at all; whereas some may have flu-like symptoms, including fever, headache, chills, and other symptoms like vomiting, jaundice, muscle aches, abdominal pain, diarrhea, etc.
Listeriosis
Listeriosis is a rare bacterial infection, which commonly affects goats, sheep and cattle. Most individuals are resistant to this infection, but people who have weakened immune system, are taking antacids, newborns, elderly or pregnant women are at increased risk of infection. This infection is usually spread through eating contaminated meat or unpasteurized milk and milk products. The infection may present symptoms such as headache, confusion, stiff neck, fever, muscle aches, loss of balance and convulsions. Pregnant women may experience flu-like symptoms, however, can lead to serious complications like miscarriage, premature delivery, stillbirth, or life-threatening infection of the baby.
Salmonellosis
Salmonellosis is a bacterial infection caused by Salmonella bacteria. These bacteria are shed in the feces of infected animals and people. Animals that usually carry the Salmonella bacteria include poultry, livestock, fish in aquariums, etc. This infection can spread to humans by eating undercooked meat, infected eggs, unpasteurized milk products, or through direct contact with infected animals or any objects touched by the infected animals. Salmonella infection can cause serious disease, particularly in young children, the elderly, and individuals with weakened immune systems. Infected individuals may experience diarrhea, fever and abdominal cramps.
Tapeworm infection
There are various types of tapeworms that can cause intestinal infections, which include beef tapeworms, pork tapeworms, and fish tapeworms. They infect people through contact with contaminated human feces found in fresh water, soil or food. Children can be infected by eating raw or uncooked meat from infected animals or fish. The contaminated food contains cysts (larval form of the tapeworm) of the parasite. Usually, children with tapeworm infection do not have any symptoms, signs may appear months or even years after the infection. These symptoms may include mild nausea, abdominal pain, weight loss, diarrhea, and other severe symptoms based on the type of tapeworm causing the infection.
The above-mentioned are just the infectious diseases that children and adults are at risk if consuming an animal-based diet. However, this diet has high content of cholesterol, esterogens, lactose, saturated fat, etc. This can cause long-term effects and increase the risk of chronic diseases like diabetes, obesity cardiovascular diseases, cancer, and other conditions. A healthy alternative to these foods is a plant-based diet. Studies have shown that adopting a plant-based diet reduces the risk of various health problems. A diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, legumes, along with vitamin B-12 supplementation is nutritionally superior to other diets. Adopting this diet at a young age can help your children live a long, healthy life.
References:
- Foodborne Germs and Illnesses. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
https://www.cdc.gov/foodsafety/foodborne-germs.html.
Accessed on May 18, 2021. - Barnard ND, Leroy F. Children and adults should avoid consuming animal products to reduce risk for chronic disease: YES. Am J Clin Nutr. 2020 Oct 1;112(4):926-930.
- Animal Transmitted Diseases. Washington State Department of Health.
https://www.doh.wa.gov/YouandYourFamily/IllnessandDisease/AnimalTransmittedDiseases.
Accessed on May 18, 2021. - Zoonotic Diseases of Cattle. Virginia Cooperative Extension Virginia State University.
https://www.pubs.ext.vt.edu/400/400-460/400-460.html.
Accessed on May 18, 2021. - Farm Animals. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
https://www.cdc.gov/healthypets/pets/farm-animals.html.
Accessed on May 18, 2021. - Food Safety. World Health Organization.
https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/food-safety.
Accessed on May 18, 2021. - Tapeworms. American Academy of Pediatrics.
https://www.healthychildren.org/English/health-issues/conditions/from-insects-animals/Pages/Tapeworms.aspx.
Accessed on May 18, 2021. - Tapeworm. Kids Health.
https://kidshealth.org/en/parents/tapeworm.html#:~:text=Kids%20with%20a%20tapeworm%20infection,to%20appendicitis%20and%20other%20problems.
Accessed on May 18, 2021. - 8 Pros and Cons of an Animal Based Diet. Health Research Foundation.
https://healthresearchfunding.org/8-pros-and-cons-of-an-animal-based-diet/.
Accessed on May 18, 2021.